“In the dimly lit hospital corridor, Jenpu Rongmei rushes to see his 12-year-old nephew Nina, only to find that he had succumbed to dengue, a disease unfamiliar to the people of Nagaland until recently. Remembering the evening vividly, Jenpu is overwhelmed by grief and disbelief at Nina’s sudden and untimely passing, reflecting on his initial optimism and the devastating impact of the mosquito-borne illness. As dengue continues to spread, claiming lives across Northeast India, Nina’s tragic death serves as a poignant reminder of the crisis fueled by climate change, leaving communities reeling with sorrow and fear.” – The Week magazine November 25, 2023
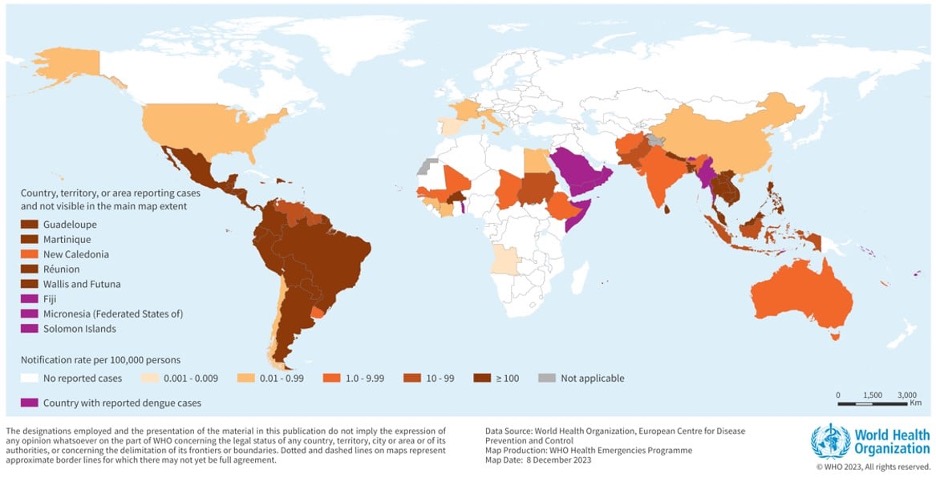
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), The global incidence of dengue has markedly increased over the past two decades, posing a substantial public health challenge. From 2000 to 2019, the World Health Organization (WHO) documented a ten-fold surge in reported cases worldwide increasing from 500 000 to 5.2 million.
An estimated 1.3 billion children globally – over one in two – live in countries where dengue outbreaks are frequent and continuous, and the situation is expected to get worse due to the climate crisis.
Several factors are associated with the increasing risk of spread of the dengue epidemic:
- The changing distribution of the vectors (chiefly Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus)
- The consequences of El Nino phenomena in 2023 and climate change leading to increasing temperatures and high rainfall, humidity
- Weakness in the surveillance systems in many affected countries may have led to delayed reporting and response and missed identification of symptoms, contributing to increased severe dengue outcomes.
- The period conducive to dengue transmission by Aedes aegypti mosquitoes has increased to 5.6 months yearly, with a 1.69% rise from 1951-1960 to 2012-2021.
Epidemiology
Dengue cases are most commonly asymptomatic or result in mild febrile illness. However, some cases will develop severe dengue, which may involve shock, severe bleeding, or severe organ impairment. This stage often starts after the fever has gone away and it is preceded by warning signs such as intense abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, bleeding gums, fluid accumulation, lethargy or restlessness, and liver enlargement.
There is no specific treatment for dengue, but the timely diagnosis of dengue cases, identification of warning signs for severe dengue, and appropriate clinical management are key elements of care to prevent the progression of severe dengue and deaths.
Dengue Situation in India
More dengue fever cases have been recorded so far in 2023 than in the last five years annually, as increasingly extreme weather events fuel the spread of the mosquito-borne illness, according to the Save the Children Organization.
Today, dengue is endemic in more than 100 countries, including India, and continues to pose a significant public health challenge. The disease’s spread underscores the importance of effective vector control measures and ongoing surveillance.
India contributes around 34% of the global burden of dengue. A meta-analysis of Indian studies estimated the dengue fatality rate to be 2.6%. Although dengue is a notifiable disease in India, studies and modeling estimates suggest that the disease is grossly underreported due to the existing gaps in the public health surveillance system.
In 2022, 230,000 infections and 303 deaths were attributed to dengue fever. However, this is likely underestimated as many cases are mild, asymptomatic, or misdiagnosed. By September 17 of the following year, India had recorded nearly 95,000 cases and 91 deaths.
These figures underscore the increasing severity of dengue fever in India over the past decade. Despite control efforts, there has been a significant increase in the number of dengue cases. However, improvements have been made in case management and reduction of the Case Fatality Rate (CFR) to below 0.5%. The rise in dengue cases highlights the urgent need for effective prevention and control measures.
Economic burden of dengue illness in India
According to a study by Dhwani Hariharan et al 2018, India’s burden of dengue in 2016 was $5.71 billion. This substantial economic impact has led to a search for innovative solutions. With the advent of Artificial Intelligence and in the field of data science, there is potential to significantly reduce the impact of the disease. By leveraging predictive modeling and real-time data analysis, these technologies can help in early detection and efficient resource allocation, thereby mitigating the burden of dengue in India.
Empowering citizens and the community using technology.
We need local plans to fight dengue – at village and city level – and with the involvement of communities. Technology and tools can be used to reduce the impact of the disease. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Accredited Social Health Activists (ASHA) workers can play a significant role in reducing the impact of dengue infection in India. AI can be used to predict dengue outbreaks by analyzing past infection data and weather trends. Machine learning algorithms can be utilized to build predictive systems for dengue, enabling timely and accurate predictions and diagnoses. This allows for early interventions and precautions to be taken, potentially reducing the spread of the disease.
ASHA workers, being the first point of contact for health-related requirements in rural areas, can play a crucial role in controlling the spread of dengue. They conduct door-to-door fever surveillance and report any occurrence of fever to the health authorities. They also create awareness about health determinants like nutrition, basic sanitation, and healthy living environments, and emphasize the importance of using health and family welfare facilities on a timely basis.
AI tools can augment ASHA workers and citizens who can identify symptoms and severity of the disease on the spot. The tool also can suggest the next step to be taken in case the severity is high or if there are symptoms. These tools can collect data for analysis and help the individual, community, and policymakers to take proactive action and hence reduce the impact of dengue. Combining historical incident data at a location, historical weather data, and weather forecasts we can provide an early warning system.
The convergence of AI and ASHA workers can lead to a more effective approach in managing dengue. AI tools can provide predictive insights about potential outbreaks, and ASHA workers can use this information for targeted interventions, awareness campaigns, and timely reporting of cases. This combined approach can significantly reduce the impact of dengue infection in the population. However, it’s important to note that the success of this approach would also depend on other factors such as the availability of resources, the level of community engagement, and the effectiveness of the health infrastructure.
At T4LK, our passionate mission is to save 1000 lives every single day. Through the power of Artificial Intelligence and data science, we’re democratizing technology to make this vision a reality. We firmly believe that the fusion of biotechnology and AI has the potential to wipe out numerous diseases, paving the way for a brighter, healthier future for all humanity.
We warmly invite you to join us in making this dream come true. Let’s join hands and work together to turn this vision into a heartfelt reality. Together, we can make a profound difference in the lives of countless individuals.
Subscribe to our newsletter to be in touch.
References:
- Dengue and dengue haemorrhagic fever: Indian perspective
- Annual-report-NVBDCP-2012 (NVBDCP)
- Dengue Situation In India
- Dengue infection in India: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Dengue fever
- Epidemiological and Entomological Investigation of Dengue Fever in Sulurpet, Andhra Pradesh, India
- How climate change is changing dengue fever
- Climate change pushes dengue into new frontiers across India
- Dengue – Global situation (WHO)
- Dengue Fever: At least 5 million cases and 5,500 deaths in horror year
- An economic evaluation of implementing a decentralized dengue screening intervention under the National Vector Borne Disease Control Programme in Tamil Nadu, South India